Rahul Beniwal, with over 15 years of experience under his belt- in software development, cloud infrastructure, product management, and systems architecture. These experiences have helped...
Server-based computing (SBC) is a solution architecture that is responsible for running applications, data storage, and processing all at the server level instead of the client device level. In this model, there is the user, using an application and an application on the other side of the network, with the server doing most of the work.
SBC makes business applications and data easily and readily available without the need for additional facilities, and the management and security are made easy and secure since all applications are within the server. As opposed to other computing paradigms, the applications in SBC do not execute on the user’s desktop or gadget. Hence, they are clients that are light or thin clients that attach or interface with actual servers to retrieve commissioned or centralized stocks.
Key components of SBC include:
- Servers: High-powered machines that host operating systems, applications, and data storage. They have the ability to manage many connections at once and also provide strong processing power. This guarantees fast performance for all users using them simultaneously.
- Clients: Lightweight terminals or computers that connect to servers to access resources. They typically demand little hardware, thus cutting down on expenses and energy use without compromising the user’s complete computing experience.
- Network infrastructure: Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs) that link clients to servers, along with routers, switches, and firewalls for traffic management. This setup is very important for making sure that connection is stable, speed of transferring information is fast enough and there are proper safety measures in place to safeguard sensitive data from any unauthorized access or theft.
- Software and Applications: Reside on servers instead of client devices, simplifying management as installations happen only one time at server level without need for additional software upkeep. They usually consist of office productivity applications, database management systems, and specialized software created for a particular organization’s requirements.
How Server-Based Computing Works
1. Client-Server Connection:
In this kind of computing setup, the client devices link up with central servers over LANs and WANs. Once they are connected, users can get into applications and data kept on the server. This means that no matter where you are physically located, your experience will remain consistent because everything is saved in one place for everyone to use. The network has a very important role as it needs to work well all the time and be fast enough so that applications respond quickly without any interruptions.
2. Data Processing and Storage:
After the client gets connected, it sends its request for server processing. The server takes care of all computational tasks such as handling data retrieval from databases or other sources, executing applications and managing storage among other things. Once the server has processed the requests of clients, it usually sends back results to them in real-time usually. This model shifts the processing load away from individual devices, enabling even less powerful clients to handle complex tasks effectively.
3. User Interaction:
For users, it seems like everything is happening smoothly. They connect to applications through a graphical user interface (GUI) that looks just like local software. This allows them to navigate and use these programs in familiar ways. The use of complex technologies such as remote desktop services and application virtualization guarantees that users can reach their applications and data without any notable delay – giving an impression of direct operation on their personal devices.
4. Centralized Management with Admin Access:
A big benefit of computing based on servers is management that’s centralized. Those who do IT administration can arrange software updates and security fixes and set up alterations for every user from only one place. This uniformity assists in keeping up with safety policies and lessens the chance of having vulnerabilities. Also, for troubleshooting and support, having a central management can make it easier. This is because, many times, problems are fixed on the server itself without requiring access to each client device. This results in less time where work is stopped and more productivity throughout the whole organization.
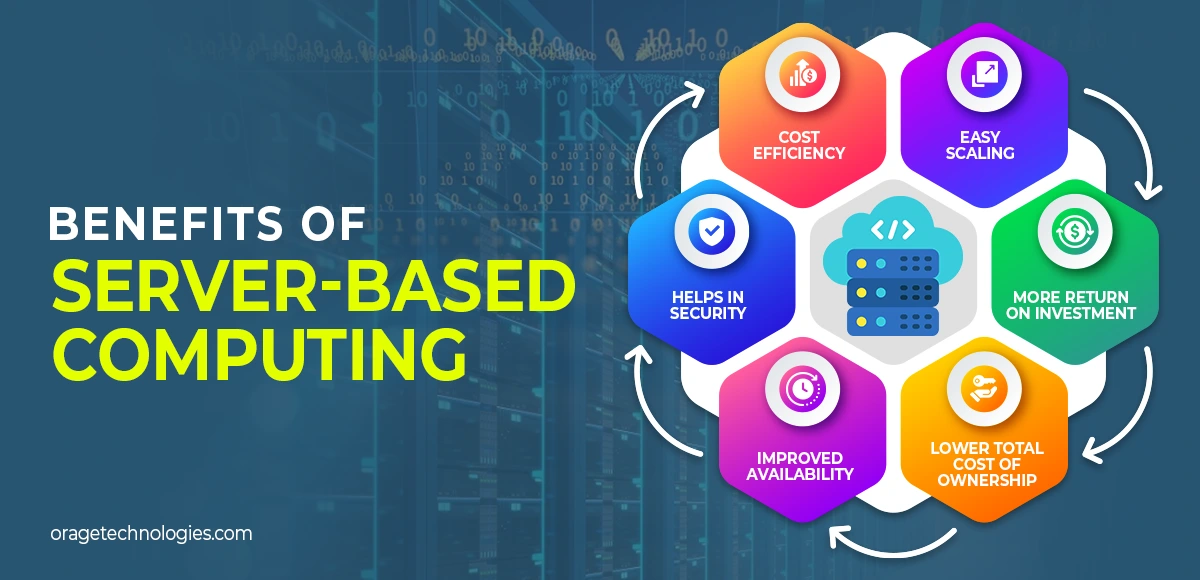
Benefits of Server-Based Computing
1. Cost Efficiency:
It’s cheaper to use server-based computing. Thin clients cost less, need fewer updates and have a longer lifespan. Moreover, with applications and data located on servers, organizations can optimize their software licensing. This means that the overall expenditure linked to managing multiple licenses across many devices is reduced.
2. Easy Scaling:
With SBC, businesses can grow their IT structure without any difficulty. As business requirements rise up, more servers could be included within the present network with less interruption to the infrastructure. This adaptability guarantees businesses can adjust to varying demands in a fast and effective manner.
For example, an e-commerce company that is experiencing a festive rush could increase the number of servers to handle the increase in traffic. This would help in maintaining a responsive and dependable website.
3. Helps in Security:
Centralizing data on servers reduces the danger of data breaches and unauthorized entry. When all important details are kept in a safe place, companies can use strong security methods like encoding, access management, and frequent backups. This method removes dependency on external storage devices which are usually at risk of being lost or stolen. Moreover, financial institutions benefit from this set up. As it significantly reduces the possibility of data theft which might happen with local storage methods.
4. Improved Availability:
Characteristics like fault tolerance and load balancing increase the dependability of server-based computing systems. These technologies make sure that applications stay accessible even if there are hardware problems or sudden increases in user need. Moreover, distributing workloads over many servers helps organizations maintain steadiness in their performance and availability.
5. Lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO):
Server-based computing can help organizations lessen their TCO by as much as 50%. Centralized management makes IT operations more efficient and decreases the requirement for extensive administrative support, thereby reducing hardware expenses.
6. More Return on Investment:
The investment in server-based computing can provide good returns because it allows existing hardware to last longer with much less maintenance. With centralized management, updates and upgrades are applied uniformly for all users, which reduces disruptions while improving productivity.
Conclusion
Server-based computing (SBC) has many benefits, which is why it’s a popular choice for organizations in different areas. Some key advantages include being cost-effective, resulting in big savings on licensing. Moreover it reduces the upkeep costs, enabling them to spend on AI and other upcoming technologies. The flexibility of SBC to scale ensured that any immediate requirements can be easily addressed. That’s why SBC is an attractive choice for firms for best from their IT resources and handle changing needs efficiently.
Also Read: Maximizing SEO Impact with AI Caption Generators

Rahul Beniwal, with over 15 years of experience under his belt- in software development, cloud infrastructure, product management, and systems architecture. These experiences have helped him design scalable solutions and businesses. He’s lived the highs and lows of entrepreneurship, guided teams through growth and change, and stayed curious about how technology continues to shape the way we work and live. In his writing, he blends deep technical insight with real-world business know-how, offering readers tools and perspectives that come from actual experience.
More Posts


